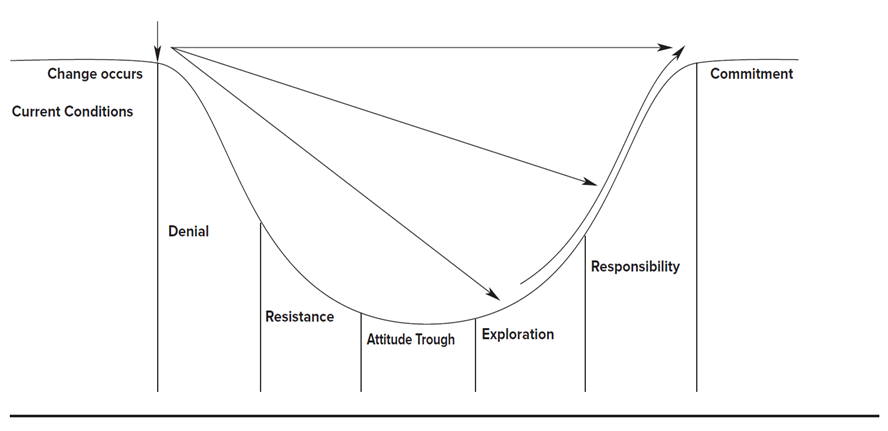
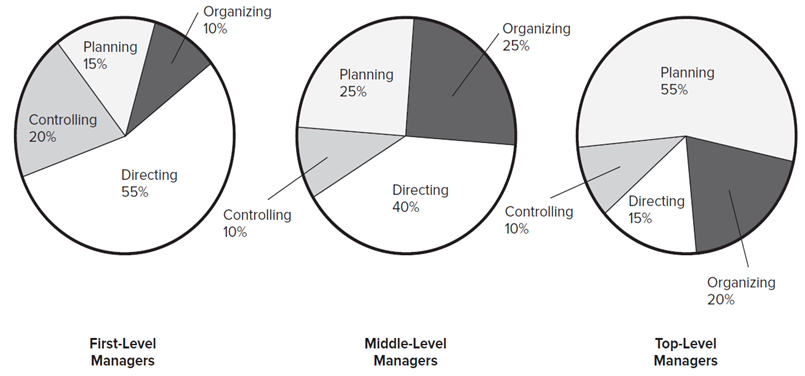
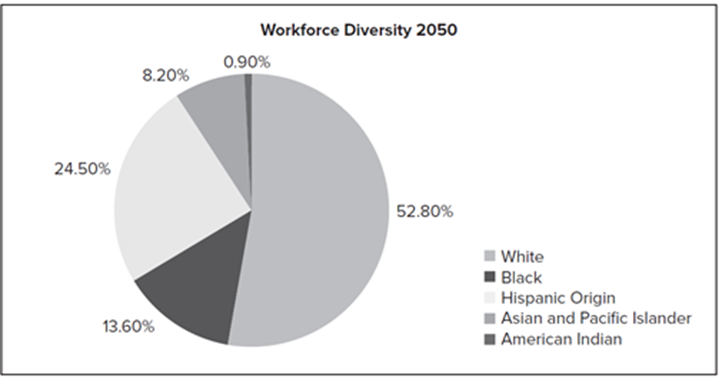
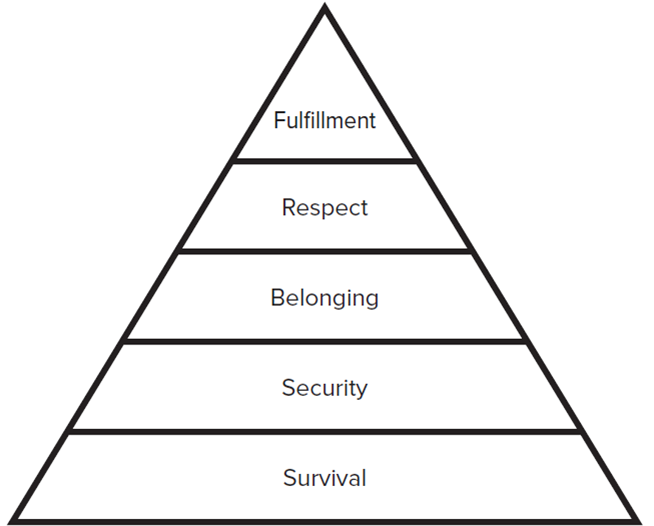
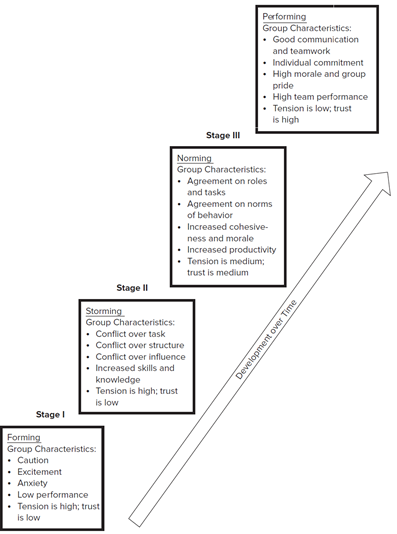
This chapter illustrates master performance management as a leadership skill and tells how to set goals, provide feedback on progress, and correct performance problems. Performance management is at the heart of leadership success and Important to have a vision, values, leadership qualities, and the power of leadership position.One-minute goal setting for performance planning: Involves identifying three to five goals that are critical to success and writing them on a single sheet of paper. Moreover, multi source evaluations can be useful for training, coaching, succession planning, and other talent management initiatives to improve performance.
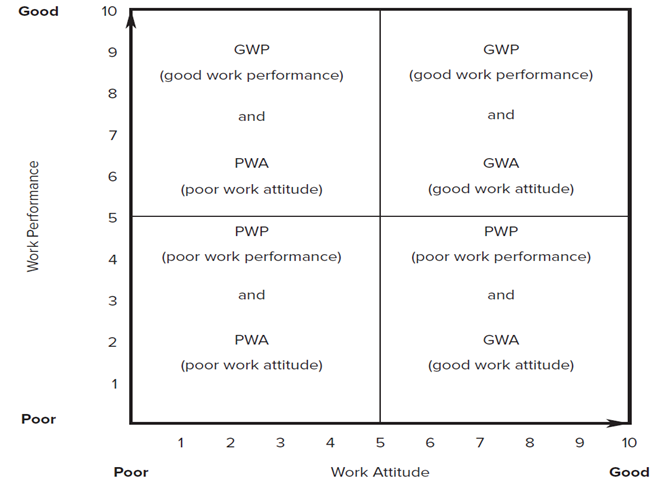
The y-axis of the graph is labeled work performance, and the x-axis is labeled work attitude. Both axes are marked from zero to ten. The beginning of both axes is marked poor, and the ends of both axes are marked good.